Detecting refrigerant gases with gas leak detectors allows an adequate monitoring of the operation of cold generation systems, both air-conditioners and refrigerators.
It is important to know how to detect refrigerant gases and that any leaks from these systems are monitored constantly. Detecting refrigerant gases has a dual goal: on the one hand it protects people and properties from the dangers arising from the leakage of refrigerant gases; on the other hand, makes it possible to ascertain the efficiency of operation of the equipment and therefore to contribute to the reduction of the operating costs of the plants.
The different refrigerant gases and the dangers of leakage
There are many refrigerant gases on the market. Some of them are no longer in use due to the potential danger to the ozone layer. Other newly developed refrigerants, on the other hand, have low Global warming potential (GWP) and a consequent level of flammability that must be monitored.
Synthetically, refrigerant gases can be grouped into:
- First generation, the so-called “freon” types, CFC and HCFC (R12, R123, R22, etc.)
- More recent, with a moderate flammability risk, HFO, (R32, R410a, R1234yf, etc.),
- Natural, hydrocarbons such as propane or methane, (CO2, NH3)
Each of them can be used for the production of cold and any leaks would involve concrete risks for people and for the safety of the plants. The risks from any leaks are also linked to the environment and the ecosystem.
The hazards associated with refrigerant gas leaks on which require focus are the following:
- Health of people: When a gas leak occurs, it gradually replaces the air we breathe. In closed and non-ventilated environments, the level of gas concentration can significantly increase and deplete breathing air. In extreme cases leading people to asphyxiation and death.
- Fire and explosion: Some refrigerant gases such as ammonia, propane and A2L are by their nature flammable. Their release corresponds to a real risk of fire and explosion if the gas comes into contact with sources of ignition.
The detection of potential gas leaks is a critical step to avoid hazard in any scenario, and requires a concrete, continuous and reliable approach.
Obligations relating to refrigerant gases and leak detection
National and international regulations regulate the use of refrigerant gases and aim to control and reduce their environmental impact. As a result, the control of leaks of these gases is now mandatory in a lot of countries.
Compliance with the standards is undoubtedly facilitated by the use of refrigerant gas detection for the systems, along with the regular maintenance and control of regulatory compliance.
In addition to the potential flammability of the new refrigerant gases, leakage control is covered by the rules already in force for the protection of areas at risk of explosion.
Regarding public places and workplaces, the advantage of such monitoring is the increased safety for staff and visitors, which will thus avoid being exposed to any gas leaks.
Practical example
Inside a supermarket, detectors placed near refrigerated shelves, cold stores or refrigerated warehouses would be able to intercept any refrigerant leaks. This also helps to monitor and protect the freshness and integrity of goods.
Furthermore, the possible escape of refrigerant gases does not only cause a risk for people and environmental damage, but also economic damage. In fact, an adequate monitoring system reduces management costs and increases safety .
The economic impact caused by refrigerant gas leaks
All refrigeration equipment is designed to perform optimally with a precise refrigerant charge. Leakage of refrigerant is not an exceptional occurrence, but rather a common occurrence . Leakage of refrigerant can cause an interruption of service or of cold production. In addition to malfunctions and excessive energy consumption , resulting in a decrease in productivity or even a general shutdown of the affected device.
On the contrary, whether the fault is at the level of the air conditioning system or the cold system in the warehouse , the use of a refrigerant gas detection system will make it possible to intervene promptly, avoiding even more costly leaks.
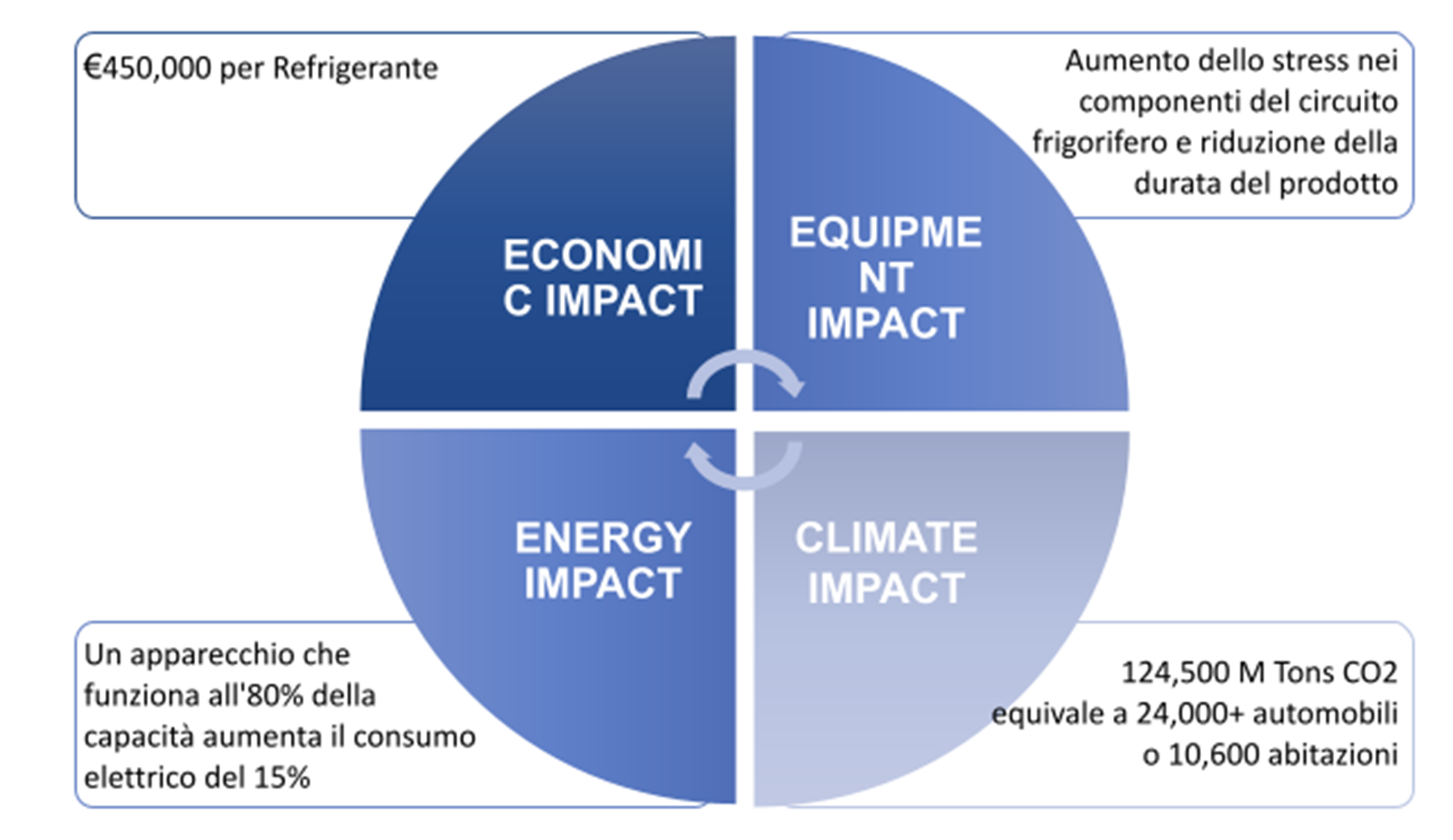
This solution also produces a reduction in the cost of recharging the refrigerant gas. This is because it allows immediate control of losses and making a real economic gain . It should in fact be borne in mind that estimates indicate that approximately 20% -25% of the refrigerant gases used in supermarkets are lost every year precisely due to gas leaks from the plants.
Also from the point of view of reducing energy consumption, detecting refrigerant gases is a winning solution. In fact, a gas leak leads to an estimated increase in energy consumption between 10% and 40%. All this generates an important cost especially for large-scale distribution activities. Even large air-conditioned spaces such as stations or airports or large refrigeration systems can have high costs.
Let’s see in this sense a theoretical example calculated precisely on a supermarket chain :
Annual calculation
- 100 supermarkets
- R-404a refrigerant gas
- 1,500 Kg per Site
- 20% Estimated loss (vs. 0%)
- Loss of 300 kg / year / site
- Average cost 15 € / Kg for R-404a
In practical terms, we are faced with an economic damage of 450,000 euros for the supermarket chain!
The refrigerant gas detectors

The SMART3-H Lite detector.
Several measuring and monitoring devices are now available that allow to check the proper operation of the refrigeration equipment . This means that the detection of any gas leaks is now guaranteed in all areas of the refrigeration industry by special detectors.
The installation of a system for the detection of refrigerant gases provides constant monitoring of any cold production plant. The installation of fixed gas detectors also meets all the obligations deriving from the regulations on refrigerant gases .
The detection of refrigerant leaks is performed by one or more gas detectors connected to a control panel, which acquires the signals from the detectors and activates alarms and commands such as ventilation systems and remote alarm signals.

The SMART3H-FM detector.
The SMART3-H LITE detectors proposed by Sensitron represent an effective solution : they can in fact be used as autonomous devices. That is, they do not need a connection to the control unit. SMART3-H LITE detectors have an integrated audible and visual alarm signal to warn in case of danger.
Environments very different from industry can also benefit from these advantages. An air-conditioned interior space in a residential context, an office or a hotel room can be equipped with these devices, declined in dimensionally discrete models, aesthetically pleasing and simple to use.
In this context, Sensitron provides the SMART3H-FM detector : designed for flush mounting, it provides constant monitoring and triggers an alarm when a refrigerant leak occurs.

